The PEPPOL Business Interoperability Specification, “BIS” from here on after, has been developed by the OpenPEPPOL AISBL Post Award Coordinating Community and is published as part of the PEPPOL specifications.
Link to main site of documentation
1. Introduction to OpenPeppol and BIS
This Peppol BIS (Business Interoperability Specification) is a result of work within the Peppol Logistics Incubation Project.
This BIS provides a set of specifications for implementing a Peppol business process. The document is concerned with clarifying requirements for ensuring interoperability of pan-European Public eProcurement and provides guidelines for supporting these requirements and how to implement them.
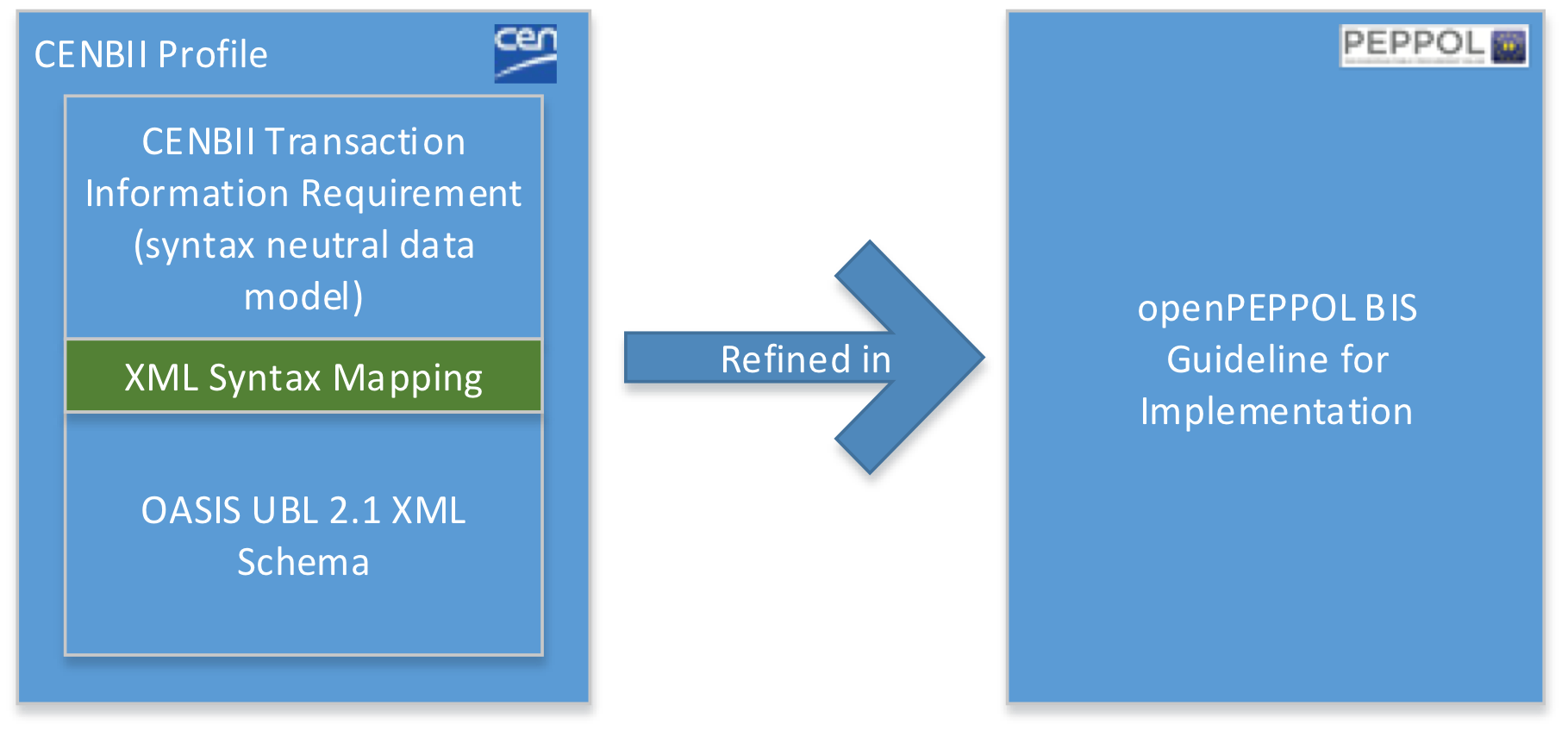
1.1. Background and objective
The Peppol BIS provides a set of specifications for implementing Peppol business documents. The specifications enable any company to issue electronic documents that fulfill legal and business processing requirement within the European Union and the EEA. It supports a subset of information that is used by most industries and enables users to issue documents (invoices, orders, despatch advices, etc…) that are valid for cross border trade within the European Union and the EEA.
The purpose of this document is to describe a common format for the Transportation Status Request and the Transportation Status message in the European market, and to facilitate an efficient implementation and increased use of electronic collaboration regarding the transportation process based on these formats.
1.2. Audience
The audience for this document is organizations wishing to be PEPPOL enabled for exchanging electronic business documents, and/or their ICT-suppliers.
These organizations may be:
-
Service providers
-
Contracting Authorities
-
Economic Operators
-
Software Developers
More specifically it is addressed towards the following roles:
-
ICT Architects
-
ICT Developers
-
Business Experts
For further information, please see PEPPOL BIS common text and introduction.
2. Principles and prerequisites
This chapter describes the principles and assumptions that underlie the use of the Transportation Status with Request.
The Transportation Status Request and the Transportation Status are used to exchange information about the status of a transport. A Transportation Status Request is used to request a transport status. A Transportation Status is used to report the status as a response to the request.
2.1. Business processes in scope
The processes covered by this profile are:
-
The Transportation Status Request is used to request the status of a transport.
-
The Transportation Status is used to report the status of a transport as a 1..1 response to a Transportation Status Request.
The main activities supported by this message are:
-
Report status on a transport based on a request for status on
-
All executions statuses for a shipment, a consignment or a transport handling unit
-
Deviations
-
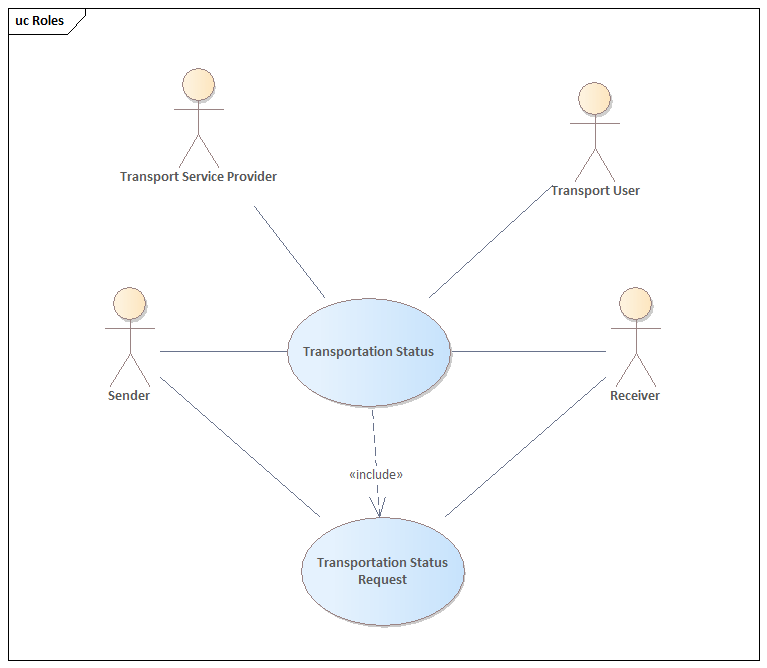
2.2. Parties and roles
The table below gives the definitions of the parties and roles involved in the Transportation Status with Request process.
| Business partners | Definition |
|---|---|
Transport User |
The Transport User is the user of the transport service, often the consignor. |
Transport Service Provider |
The Transport Service Provider is the provider of the transprot services, often the carrier. |
| Role/actor | Definition |
|---|---|
Sender (cac:SenderParty) |
The sender of the Transportation Status Request or Transportation Status. |
Receiver (cac:ReceiverParty) |
The receiver of the Transportation Status Request or Transportation Status. |
The diagram below shows the roles in the Transportation Status with Request process.
3. Processes and use cases
3.1. Legend for BPMN diagrams
The diagrams are expressed in the BPMN notation. The diagram below serves as an explanation for the diagrams used in the process descriptions.
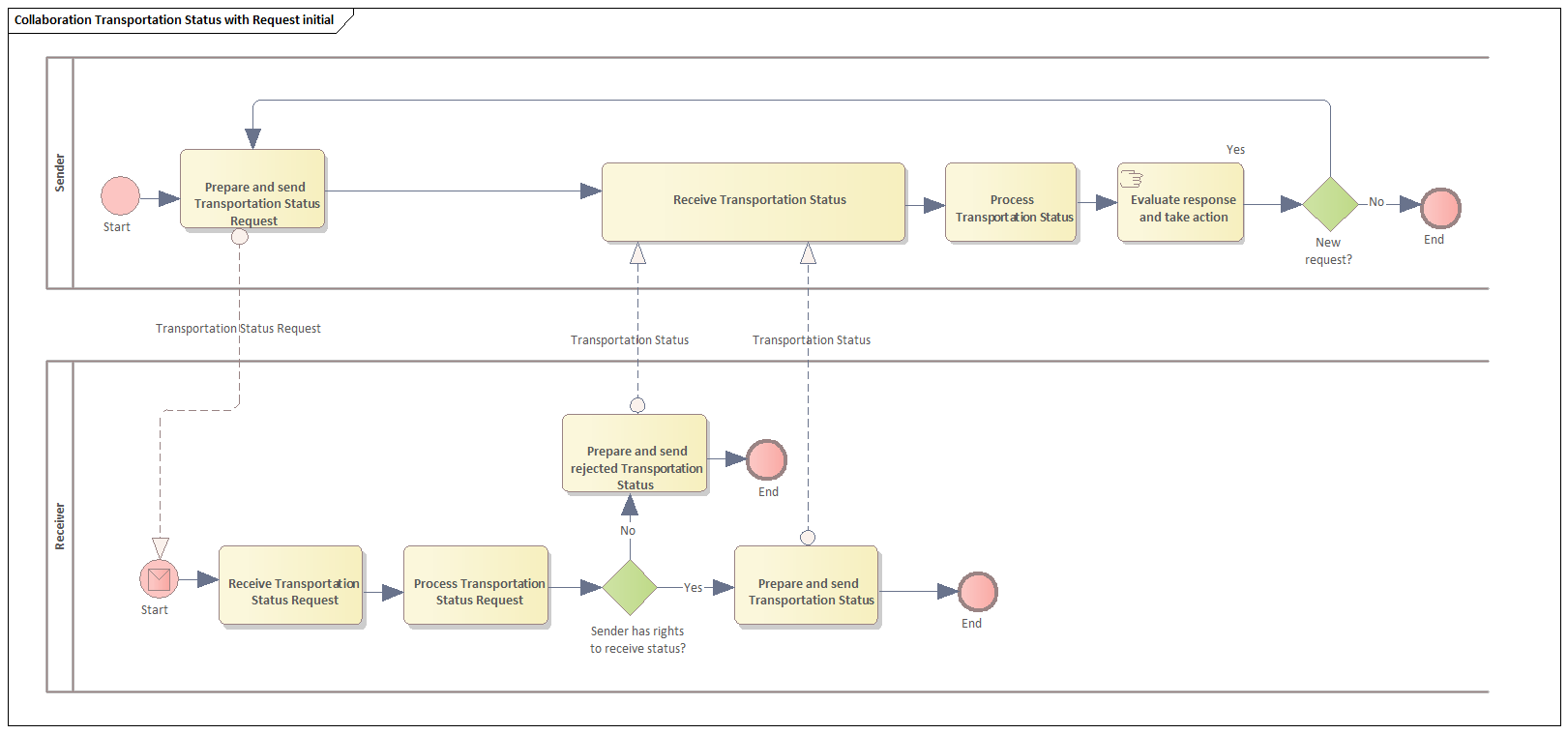
The following section and diagrams show the choreography of the business process involving various parties.
3.2. Request for transportation status
The following diagram shows a process where the transport user or anyone having the rights to request and receive a status sends a Transportation Status Request to the transport service provider who responds with a Transportation Status. The different types of requests that can be sent are described in chapter 3.3 Typical use cases.
Parties involved:
-
The Sender of the Transportation Status Request and Receiver of the Transportation Status can either be the party that has booked the transport (Transport User) or any other party involved in the trade and who has the rights to receive the status that is requested.
-
The Receiver of the Transportation Status Request and Sender of the Transportation Status is normally the Transport Service Provider (Carrier or Freight Forwarder).
3.3. Typical use cases
3.3.1. Use case 1 – Request for status on a specific transport event
| Use Case Number | 1 |
|---|---|
Use Case Name |
Request for status on a specific transport event. |
Use Case Description |
The Sender sends a Transportation Status Request to ask for status on a specific transport event. The Transportation Status Type Code must be set to 4 (All execution statues) and the event must be specified under Consignment/Transport Event. |
Parties involved |
Sender |
Assumptions |
The transport is agreed in a Transport Execution Plan or similar document. The sender of the Transportation Status Request has the rights to receive the type of status that is requested. |
The flow |
|
XML example file |
See Examples files Appendix A for sample files illustrating Use Case 1. |
3.3.2. Use case 2 – Request for status on all transport events
| Use Case Number | 2 |
|---|---|
Use Case Name |
Request for status on all transport events. |
Use Case Description |
The Sender sends a Transportation Status Request to ask for status on all transport events up to date including the current status of the transport. The Transportation Status Type Code must be set to 4 (All execution statues). |
Parties involved |
Sender |
Assumptions |
The transport is agreed in a Transport Execution Plan or similar document. The sender of the Transportation Status Request has the rights to receive the type of status that is requested. |
The flow |
|
XML example file |
See Examples files Appendix A for sample files illustrating Use Case 2. |
3.3.3. Use case 3 – Request for status on a specific transport handling unit
| Use Case Number | 3 |
|---|---|
Use Case Name |
Request for status on a specific transport handling unit. |
Use Case Description |
The Sender sends a Transportation Status Request to ask for status on a specific transport handling unit. The Transportation Status Type Code must be set to 4 (All execution statues) and the transport handling unit must be specified under Consignment/TransportHandlingUnit. |
Parties involved |
Sender |
Assumptions |
The transport is agreed in a Transport Execution Plan or similar document. The sender of the Transportation Status Request has the rights to receive the type of status that is requested. |
The flow |
|
XML example file |
See Examples files Appendix A for sample files illustrating Use Case 3. |
3.3.4. Use case 4 – Request for status on deviations
| Use Case Number | 4 |
|---|---|
Use Case Name |
Request for status on deviations. |
Use Case Description |
The Sender sends a Transportation Status Request to ask for deviations on all transport events. The Transportation Status Type Code must be set to 3 (Deviations) and the reason for the deviations must be stated in the Transportation Execution Status Code with addtional information in Description. |
Parties involved |
Sender |
Assumptions |
The transport is agreed in a Transport Execution Plan or similar document. The receiver of the Transportation Status has an agreement to get the status being sent. |
The flow |
|
XML example file |
See Examples files Appendix A for sample files illustrating Use Case 4. |
4. Semantic datatypes
Semantic data types are used to bridge the gap between the semantic concepts expressed by the information elements and the technical implementation. The semantic data types define the allowed value domain for the content, and any additional information components (attributes) needed in order to ensure its precise interpretation.
4.1. Primitive types
Semantic data type content may be of the following primitive types. These primitive types were taken from ISO 15000-5:2014, Appendix A.
| Primitive type | Definition |
|---|---|
Binary |
A set of finite-length sequences of binary digits. |
Date |
Time point representing a calendar day on a time scale consisting of an origin and a succession of calendar ISO 8601:2004. |
Decimal |
A subset of the real numbers, which can be represented by decimal numerals. |
String |
A finite sequence of characters. |
4.2. Semantic data types
The different semantic data types are described in the tables below, where various features such as attributes, format, and decimals as well as the basic type are defined for each semantic data type. They are based on ISO 15000-5:2014.
When used in an instance document, each data element will contain data. In the below tables this is identified as the “content”. Whenever a business term is used this term shall always have content and therefore the content is always mandatory.
4.2.1. Amount
An amount states a numerical monetary value. The currency of the amount is defined as a separate business term.
| Amount is floating up to two fraction digits. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Decimal |
10000.25 |
4.2.2. Price Amount
A price amount states a numerical monetary amount value for data elements that contain item prices that may be multiplied by item quantities. The currency of the amount is defined as a separate business term.
| Unit price amount does not set restrictions on number of decimals, as contrast to the Amount type |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Decimal |
10000.1234 |
4.2.3. Percentage
Percentages are given as fractions of a hundred (per cent) e.g. the value 34.78 % in percentage terms is given as 34.78.
| No restriction on number of decimals for percentages. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Decimal |
34.7812 |
4.2.4. Quantity
Quantities are used to state a number of units such as for items. The code for the Unit of Measure is defined as a separate business term.
| No restriction on number of decimals for quantities. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Decimal |
10000.1234 |
4.2.5. Code
Codes are used to specify allowed values in elements as well as for lists of options. Code is different from Identifier in that allowed values have standardized meanings that can be known by the recipient.
| Codes shall be entered exactly as shown in the selected code list |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
String |
Abc123 |
4.2.6. Identifier
Identifiers (IDs) are keys that are issued by the sender or recipient of a document or by a third party.
| The use of the attributes is specified for each information element. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
String |
abc:123-DEF |
Scheme identifier |
Conditional |
String |
0088 |
Scheme version identifier |
Conditional |
String |
1.0 |
4.2.7. Date
Dates shall be in accordance to the “Calendar date complete representation” as specified by ISO 8601:2004, format YYYY-MM-DD.
| Dates shall not include timezone information. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Date |
2017-12-01 |
4.2.8. Time
Time shall be in accordance to the “Extended time format” as specified by ISO 8601:2004, format [hh]:[mm]:[ss].
| Time shall not include timezone information. Decimal fraction on seconds SHALL not be used. |
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Date |
09:30:12 |
4.2.9. Document Reference
Document Reference Types are identifiers that were assigned to a document or document line.
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
String |
abc:123-DEF |
4.2.10. Text
Text is the actual wording of anything written or printed. Line breaks in the text may be present, and any line breaks should be preserved and respected by the receiver’s system
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
String |
5% allowance when paid within 30 days |
4.2.11. Binary objects
Binary objects can be used to describe files which are transmitted together with the business document. Attachments shall be transmitted together with the business document. The binary object has two supplementary components: a Mime Code, which specifies the Mime type of the attachment and a Filename that is provided by (or on behalf of) the sender of the business document.
| Component | Use | Primitive Type | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
Content |
Mandatory |
Binary |
QmFzZTY0IGNvbnRlbnQgZXhhbXBsZQ== |
Mime Code |
Mandatory |
String |
image/jpeg |
Filename |
Mandatory |
String |
drawing5.jpg |
5. Code lists
5.1. Code lists for coded elements
Any element with the semantic data type = code, can mandate the use of a specific code list (or a fixed value). The applicable code lists can be found under Code lists in the top-menu bar. There you can find the valid codes, their names and description, and also links to where the same code list is used elsewhere in the transaction, or in other Logistics documents. Below are examples on usage of code lists for identifiers being used in all formats.
5.2. Code list for identifiers - Examples of usage
5.2.1. Party identifiers and party legal registration identifier scheme
All party identifiers (cac:PartyIdentification/cbc:ID) and party legal registration identifier (cac:PartyLegalEntity/cbc:CompanyID) has an optional scheme identifier attribute (@schemeID).
If used, the value shall be chosen from the ICD code list.
cac:PartyIdentification<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="0088">5790000435968</cbc:ID> (1)
</cac:PartyIdentification>| 1 | schemeID attribute is optional, but when used, the codes must be from the ICD code list. |
5.2.2. Electronic address identifier scheme identifier
All electronic address identifiers (cbc:EndpointID/@schemeID) use the Electronic Address Scheme code list (EAS),
maintained by CEF.
Valid values are found in the EAS code list.
cbc:EndpointID<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="0184">DK87654321</cbc:EndpointID> (1)| 1 | schemeID attribute is mandatory |
6. Description of selected parts of the Transportation Status Request and Transportation Status
6.1. Parties
The following parties/roles may be specified in the transactions. The same actor may play more than one role depending on the handling routine.
6.1.1. Sender (SenderParty)
The sender of the Transportation Status Request or Transportation Status.
Example:
<cac:SenderParty>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="0198">10154596</cbc:EndpointID>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="0088">7300010000001</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>DHL Express</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Jydekrogen 14</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Indkørsel 5</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Vallensbæk Landsby</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>2625</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>Region Hovedstaden</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:AddressLine>
<cbc:Line>Bygning 5</cbc:Line>
</cac:AddressLine>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode>DK</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID>GB325456788</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cbc:RegistrationName>Consortial</cbc:RegistrationName>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="0089">SC234567</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:RegistrationAddress>
<cbc:CityName>Farthing</cbc:CityName>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode>GB</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:RegistrationAddress>
</cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cac:Contact>
<cbc:Name>Mrs Receiver</cbc:Name>
<cbc:Telephone>0158 1233714</cbc:Telephone>
<cbc:ElectronicMail>msreceiver@tplogistics.co.uk</cbc:ElectronicMail>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:SenderParty>6.1.2. Receiver (ReceiverParty)
The receiver of the Transportation Status Request or Transportation Status.
Example:
<cac:ReceiverParty>
<cbc:EndpointID schemeID="0198">41955619</cbc:EndpointID>
<cac:PartyIdentification>
<cbc:ID schemeID="0088">7300010000001</cbc:ID>
</cac:PartyIdentification>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>Leman</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Ventrupvej 6</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Greve Landsby</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Greve</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>2670</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>Region Sjælland</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:AddressLine>
<cbc:Line>Bygning 5</cbc:Line>
</cac:AddressLine>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode>DK</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cbc:CompanyID>GB325456788</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:TaxScheme>
<cbc:ID>VAT</cbc:ID>
</cac:TaxScheme>
</cac:PartyTaxScheme>
<cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cbc:RegistrationName>Consortial</cbc:RegistrationName>
<cbc:CompanyID schemeID="0089">SC234567</cbc:CompanyID>
<cac:RegistrationAddress>
<cbc:CityName>Farthing</cbc:CityName>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode>GB</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:RegistrationAddress>
</cac:PartyLegalEntity>
<cac:Contact>
<cbc:Name>Mr Sender</cbc:Name>
<cbc:Telephone>0158 1233714</cbc:Telephone>
<cbc:ElectronicMail>sender@consignor-company.co.uk</cbc:ElectronicMail>
</cac:Contact>
</cac:ReceiverParty>6.2. Document identification
The Transportation Status Request and the Transportation Status are identified by the Document ID on header level.
Example:
<cbc:ID>TS_1</cbc:ID>6.3. Shipping order ID
The Shipping order ID refers to the shipping order that the status is to be reported on.
Example:
<cbc:ShippingOrderID>KHN23-44044</cbc:ShippingOrderID>6.4. Transportation status codes
The Transportation status type code identifies the type of status that is requested. The following codes can be used:
-
3=Deviations
-
4=All execution statues
The Transport Execution Status Code is used in the Transportation Status to identify the actual status on the shipment, consignment or transport handling unit that is being reported. Codes according to code list.
Example:
<cbc:TransportationStatusTypeCode listID="TrStatus1">3</cbc:TransportationStatusTypeCode>
<cbc:TransportExecutionStatusCode>35</cbc:TransportExecutionStatusCode>6.5. Transport event
Transport Event on header level is only included in the Transportation Status to report status on all transport events during the transport. Identification, date and time of the event must be stated, and a Transport Event Type Code may be used to detail the status. A signature may also be added to the transport event status.
Example:
<cac:TransportEvent>
<cbc:IdentificationID>1234</cbc:IdentificationID>
<cbc:OccurrenceDate>2023-06-06</cbc:OccurrenceDate>
<cbc:OccurrenceTime>09:29:30+01:00</cbc:OccurrenceTime>
<cbc:TransportEventTypeCode>1</cbc:TransportEventTypeCode>
<cac:Signature>
<cbc:ID>3453</cbc:ID>
<cbc:ValidationDate>2021-09-29</cbc:ValidationDate>
<cbc:ValidationTime>09:49:00+01:00</cbc:ValidationTime>
<cac:SignatoryParty>
<cac:PartyName>
<cbc:Name>HUS Hospital</cbc:Name>
</cac:PartyName>
<cac:PostalAddress>
<cbc:StreetName>Topeliuksenkatu 5</cbc:StreetName>
<cbc:AdditionalStreetName>Purchasing</cbc:AdditionalStreetName>
<cbc:CityName>Helsinki</cbc:CityName>
<cbc:PostalZone>00260</cbc:PostalZone>
<cbc:CountrySubentity>Heremouthshire</cbc:CountrySubentity>
<cac:AddressLine>
<cbc:Line>Gate 34</cbc:Line>
</cac:AddressLine>
<cac:Country>
<cbc:IdentificationCode>FI</cbc:IdentificationCode>
</cac:Country>
</cac:PostalAddress>
<cac:Person>
<cbc:ID schemeID="zzz">45976</cbc:ID>
<cbc:FirstName>Valiry</cbc:FirstName>
<cbc:FamilyName>Sender</cbc:FamilyName>
<cbc:JobTitle>Director</cbc:JobTitle>
</cac:Person>
</cac:SignatoryParty>
<cac:DigitalSignatureAttachment>
<cbc:EmbeddedDocumentBinaryObject mimeCode="application/pdf" filename="Hours-spent.pdf">aHR0cHM6Ly90ZXN0LXZlZmEuZGlmaS5uby9wZXBwb2xiaXMvcG9hY2MvYmlsbGluZy8zLjAvYmlzLw==</cbc:EmbeddedDocumentBinaryObject>
<cac:ExternalReference>
<cbc:URI>www.beast.se</cbc:URI>
</cac:ExternalReference>
</cac:DigitalSignatureAttachment>
</cac:Signature>
</cac:TransportEvent>6.6. Consignment
In this profile consignment is used to identify any transport events or transport handling units that it is requested status on.
Example:
<cac:Consignment>
<cbc:ID>12535157654567654</cbc:ID>
<cac:Status>
<cbc:ConditionCode listID="zzz">4</cbc:ConditionCode>
<cbc:Description>Description</cbc:Description>
</cac:Status>
<cac:TransportEvent>
<cbc:IdentificationID>21412312412</cbc:IdentificationID>
<cbc:OccurrenceDate>2023-06-01</cbc:OccurrenceDate>
<cbc:OccurrenceTime>10:23:34</cbc:OccurrenceTime>
<cbc:TransportEventTypeCode>1</cbc:TransportEventTypeCode>
<cac:Period>
<cbc:StartDate>2021-09-25</cbc:StartDate>
<cbc:StartTime>12:00:00</cbc:StartTime>
<cbc:EndDate>2021-09-27</cbc:EndDate>
<cbc:EndTime>12:00:00</cbc:EndTime>
</cac:Period>
</cac:TransportEvent>
<cac:TransportHandlingUnit>
<cbc:ID schemeID="sscc">11111222222222</cbc:ID>
<cac:Status>
<cbc:ConditionCode listID="zzz">4</cbc:ConditionCode>
<cbc:Description>Package with id 2342556523 is damaged</cbc:Description>
</cac:Status>
</cac:TransportHandlingUnit>
</cac:Consignment>7. Peppol Identifiers
PEPPOL has defined a PEPPOL Policy for identifiers, policy 8 that specifies how to use identifiers in both its transport infrastructure and within the documents exchanged across that infrastructure. It also introduces principles for any identifiers used in the PEPPOL environment. The policies that apply to this BIS are the following:
7.1. Profiles and messages
All messages contains ProfileID and CustomizationID. ProfileID identifies what business process a given message is part of, and CustomizationID identifies the kind of message and the rules applied.
Profiles are connected to one business process, and may contain multiple document types. Valid document instances shall contain corresponding ProfileID and CustomizationID.
| CustomizationID is a string without spaces. The list below contains spaces in CustomizationID to make them easier to read. Make sure to remove any spaces before use. |
7.2. Customization and Profile identifiers
In the table below you will find the values to be used as the specification identifier and the business process type for this profile.
| Type | Element cbc:CustomizationID |
Element cbc:ProfileID |
|---|---|---|
Transportation status request (Trdm126) |
urn:fdc:peppol.eu:logistics:trns:transportation_status_request:1 |
urn:fdc:peppol.eu:logistics:bis:transportation_status_w_request:1 |
Transportation status (Trdm127) |
urn:fdc:peppol.eu:logistics:trns:transportation_status:1 |
7.3. Namespaces
The Transportation Status Request data model is bound to UBL 2.3 of the document type {ubl-transportation-status-request}. The target namespace for the UBL2.3 TransportationStatusRequest is: urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:TransportationStatusRequest-2
The Transportation Status data model is bound to UBL 2.3 of the document type {ubl-transportation-status}. The target namespace for the UBL2.3 TransportationStatus is: urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:TransportationStatus-2
